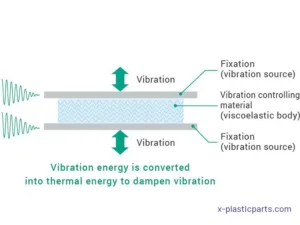
Vibration damping material plays a key role in absorbing and dissipating the energy generated by these vibrations. These materials are specifically designed to convert vibrational energy into a small amount of heat, thereby reducing the amplitude of the vibrations and minimizing their impact.
In this post, we will explore the most common vibration damping materials, their properties, and their typical applications. Understanding these materials and their appropriate use can help in selecting the right solutions for specific needs, ensuring improved performance, safety, and comfort in various settings.
What is Vibration Damping?
Vibration damping refers to the process of reducing or eliminating unwanted oscillations in a mechanical system. It involves the use of materials and techniques designed to absorb and dissipate the energy generated by vibrations, thereby minimizing their impact. The primary purpose of vibration damping is to enhance the performance, safety, and longevity of machinery, structures, and various devices by mitigating the adverse effects of these oscillations.
Vibration damping is crucial in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, manufacturing, and transportation.
In the next sections, we will explore the common vibration damping materials.
1. Vibration Damping Material – Rubber
Rubber is considered one of the best vibration damping materials , because it quickly absorbs vibration energy and converts it to heat. It has a relatively high shear modulus which allows it to dampen vibrations effectively.
Best Rubber Material Properties and Advantages
- High elasticity and flexibility.
- Excellent vibration and shock absorption.
- Good durability and resistance to abrasion and impact.
- Resistant to various environmental factors (e.g., weather, chemicals).
Types of Rubbers for Best Vibration Damping
- Natural Rubber: Derived from latex of rubber trees, known for its high elasticity and tensile strength.
- Neoprene Rubber: A synthetic rubber with excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance.
- Silicone Rubber: Known for its wide temperature range, flexibility, and durability.
Rubber Molding Common Applications
- Automotive parts (e.g., engine mounts, bushings).
- Industrial machinery (e.g., vibration isolators, pads).
- Consumer products (e.g., footwear, sports equipment).
2.Vibration Damping Material – Polyurethane
Polyurethane materials are exceptionally versatile, durable, and resilient for vibration dampening material. They can be custom-engineered to meet specific application requirements. Polyurethane exhibits viscoelastic properties, absorbing vibration energy through its elastic-viscous behavior. It is available in various forms, including flexible foam, rigid foam, and elastomers, each suitable for different applications.
PU Material Properties and Advantages
- Versatility: Available in multiple forms (foams, elastomers).
- Energy Absorption: Superior shock absorption and vibration damping.
- Durability: High resistance to abrasion, impact, and chemicals.
- Temperature Stability: Performs well across a range of temperatures.
Types of Polyurethane for Vibration Damping
- Flexible Polyurethane Foam: Soft and cushioning, ideal for comfort and protective applications.
- Rigid Polyurethane Foam: Hard and structural, used for insulation and structural components.
- Polyurethane Elastomers: Highly elastic and durable, used in demanding applications.
Urethane Material Common Applications:
- Packaging: Protects sensitive items during transport.
- Automotive: Suspension components, seat cushions.
- Construction: Insulation, Urethane seal gaskets.
- Sports Equipment: Protective gear and padding.
3. Vibration Damping Material – Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC sheets act as sound barriers that dampen vibrations on enclosure surfaces due to their superior chemical resistance and ability to absorb vibrations quickly. It is a cost-effective material.
PVC Material Properties and Advantages:
- Durability: High resistance to wear, chemicals, and weathering.
- Flexibility: Can be made flexible or rigid depending on the formulation.
- Cost-Effective: Relatively low cost compared to other damping materials
- Fire Resistance: Naturally flame retardant.
Types of PVC for Vibration Damping
- Flexible PVC: Used for flexible applications like hoses and cables.
- Rigid PVC: Used for construction materials like pipes and panels.
PVC Damping Material for Vibration Common Applications:
- Construction: Pipes, conduit, and building materials.
- Electronics: Cable insulation and connectors.
- Automotive: Interior trim and seals.
- Consumer Goods: Flooring, toys, and medical devices.
4. Vibration Damping Material – Viscoelastic Polymers
Materials that absorbs vibration like Sorbothane, which is a polyether-based polyurethane, exhibit viscoelastic vibration damping properties. They combine shock absorption, vibration isolation, and damping characteristics, making them efficient acoustic dampers and absorbers.
Viscoelastic Polymers Properties and Advantages:
- Viscoelasticity: Combines properties of both liquids and solids.
- Energy Dissipation: Excellent at absorbing and dissipating energy.
- Durability: Long-lasting and stable performance.
- Temperature Performance: Effective over a broad temperature range.
Types of Viscoelastic Polymers for Vibration Absorbing:
- Sorbothane: A widely used viscoelastic material known for superior damping properties.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Combine properties of rubber and plastic, versatile and effective.
Vibration Absorbing Material Common Applications:
- Electronics: Vibration damping in sensitive components.
- Footwear: Insoles for shock absorption.
- Industrial Machinery: Vibration isolators and pads.
- Medical Devices: Cushioning and support components.
5. Vibration Damping Material – Metal Alloys
Metal alloys are used in applications requiring both structural support and vibration damping. They combine the stiffness of metals with the damping properties of other materials.
Vibration Absorbing Material Properties and Advantages:
- Stiffness and Strength: Provide structural support while damping vibrations.
- Durability: High resistance to wear, fatigue, and environmental factors.
- Temperature Stability: Maintain properties across a wide temperature range.
- Energy Dissipation: Effective at converting vibrational energy to heat.
Types of Metal Alloys for Dampening:
- Constrained Layer Damping (CLD) Materials: Combine a viscoelastic layer with metal layers for enhanced damping.
- Shape Memory Alloys (SMA): Alloys like Nitinol that can return to a pre-deformed shape.
Vibration Dampening Material Common Applications:
- Aerospace: Structural components that reduce vibration and noise.
- Automotive: Engine mounts, exhaust systems.
- Construction: Bridges, buildings, and other infrastructure.
- Industrial Machinery: Heavy equipment components that need both strength and damping.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Vibration Damping Material
Selecting the appropriate vibration damping material requires a thorough understanding of the specific conditions and requirements of the application. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Frequency and Amplitude of Vibrations
- Frequency: Different materials perform better at different vibration frequencies. High-frequency vibrations may require different damping materials compared to low-frequency vibrations.
- High-Frequency Vibrations: Materials like viscoelastic polymers (e.g., Sorbothane) are effective.
- Low-Frequency Vibrations: Heavy-duty rubbers and metal composites may be more suitable.
- Amplitude: The extent of vibration displacement (amplitude) also influences the choice of material. Materials must be able to handle the expected amplitude without degrading or failing.
2. Environmental Conditions
- Temperature: The operating temperature range is crucial. Some materials like silicone rubber perform well in extreme temperatures, while others may lose effectiveness.
- Humidity: Moisture can affect some damping materials, leading to degradation or loss of damping properties. Materials like neoprene rubber are more resistant to moisture.
- Exposure to Chemicals: In industrial environments, exposure to oils, solvents, and other chemicals can impact material performance. Neoprene and polyurethane are known for their chemical resistance.
3. Load and Stress Factors
- Static and Dynamic Loads: The material must withstand both the static load (constant weight or force) and dynamic loads (varying forces during operation).
- Stress and Strain: The material’s ability to deform under stress and return to its original shape is critical. Materials with high elasticity and flexibility, like natural rubber, are suitable for high-stress applications.
4. Cost Considerations
- Material Costs: The cost of raw materials varies significantly. Budget constraints may influence the choice of damping material.
Vibration Damping Material Conclusion
Vibration damping is a critical requirement across numerous industries to ensure the longevity, performance, and safety of machinery, structures, and systems. The appropriate vibration damping material is crucial for effective vibration control and mitigation. This article has explored the different types of vibration damping material, and each material offers unique properties and characteristics.
By leveraging the right vibration damping materials and techniques, industries can mitigate the detrimental effects of vibrations, improve operational efficiency, extend component lifespan, and enhance overall safety and comfort.
FAQ with Vibration Absorbing Material
The best material for vibration damping depends on the specific application and the criteria mentioned previously. Rubber, Polyurethane, Viscoelastic polymers, metal composites, PVC, all are the best materials for the specific application requirements and operating conditions.
Vibration Absorbing is often used interchangeably with damping. The fine distinction is that damping emphasizes the conversion and dissipation of energy while absorbing focuses on the material’s ability to take in and reduce vibrations.